https://www.ketogenic-diet-resource.com/medical-research.html
Ketogenic Diet and Microbiota: Friends or Enemies?
Антропология/Эволюция
Body size downgrading of mammals over the late Quaternary Животные значительно уменьшились в размерах за последние 2 миллиона лет.
Наши предки были карниворами не более 50,000 лет тому назад. Ели больших животных.
Miki Ben-Dor PhD
Мясо в рационе человека: антропологическая перспектива
Карнивор
снижение клетчатки благоприятно влияет на запоры
The Role of Fiber in Energy Balance
Stopping or reducing dietary fiber intake reduces constipation and its associated symptoms
Reduction of phytic acid and enhancement of bioavailable micronutrients in food grains
Health Implications of Beef Intramuscular Fat Consumption Troy et al 2016
Uric acid and glutathione levels during short-term whole body cold exposure.

Процессы кетоза
Cahill’s starvation study: Liver and kidney metabolism during prolonged starvation (Owen et al., 1969)
β-hydroxybutyrate: Much more than a metabolite John C. Newman and Eric Verdin
Ketoacids? Good medicine? George F. Cahill, Jr and Richard L. Veech 2003
Ketone body metabolism and cardiovascular disease
Альцгеймер
APOE ε4, the door to insulin-resistant dyslipidemia and brain fog? A case study.
Свободные радикалы
The two faces of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in adipocyte function and dysfunction
«a high-carbohydrate meal may evoke a greater postprandial oxidative stress response, whereas both fat and carbohydrate increased IL6. We speculate that the observed increases in postprandial IL6, without increases in any other markers of inflammation, may indicate a normal IL6 response to enhance glucose uptake, similar to its role postexercise.»
Reactive oxygen species, nutrition, hypoxia and diseases: Problems solved?
How mitochondria produce reactive oxygen species
Hydrogen peroxide: a Jekyll and Hyde signalling molecule
β-Hydroxybutyrate Elicits Favorable Mitochondrial Changes in Skeletal Muscle
Долголетие
Беременность
Direct toxicity of insulin on the human placenta and protection by metformin
Спорт
Ketogenic diet does not affect strength performance in elite artistic gymnasts
Anticatabolic Effects of Ketone Bodies in Skeletal Muscle
Неалкогольное ожирение печени
меньше фруктозы — меньше жира в печени
Онко
CANCER and KD on people Dr Colin Champ: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24442482 (2014)
(1913!) JMR, Van Ness, E «The effect of the non-carb diet upon the growth of sarcomea in rats» LArge study.
P. Goodwin breast cancer https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11773152
5 years, higher insulin worse outcomes..
Emond JA «Risk of breast cancer reccurence assoc. with carb intake» 2014 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24755714
hi carb diet 500% more risk than low carb…
Anti-tumor FX of KD, meta analysis: 45% risk in death on KD. Diet is effective before cancer was given to mice and undergoing treatment. Not by itself.
PI3K inhibitor (blocks insulin), fights cancer (but the diet worked better). https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-018-0343-4
No randomized human studies on cancer yet.
video: https://blog.virtahealth.com/dr-colin-champ-diet-cancer-warburg/
Press-pulse: a novel therapeutic strategy for the metabolic management of cancer Thomas N. Seyfried George Yu, Joseph C. Maroon and Dominic P. D’Agostino
Атеросклероз, связь насыщенного жира и риск ссз
Omega-6 vegetable oils as a driver of coronary heart disease: the oxidized linoleic acid hypothesis
An Increase in the Omega-6/Omega-3 Fatty Acid Ratio Increases the Risk for Obesity
Dr. David Ludwig MD PHD. https://www.drdavidludwig.com/scientific-research/
https://www.bmj.com/content/363/bmj.k4583 20 weeks, randomized, controlled. same calories — low-carb — more energy burned.
The PURE Study,: largest-ever epidemiological study, contradicts diet-heart hypothesis
Associations of fats and carbohydrate intake with cardiovascular disease and mortality in 18 countries from five continents (PURE): a prospective cohort study
The Lancet (2017)
Mahshid Dehghan, Andrew Mente, Xiaohe Zhang, et al., on behalf of the Prospective Urban Rural Epidemiology (PURE) study investigators*
Interpretation of findings: “High carbohydrate intake was associated with higher risk of total mortality, whereas total fat and individual types of fat were related to lower total mortality. Total fat and types of fat were not associated with cardiovascular disease, myocardial infarction, or cardiovascular disease mortality, whereas saturated fat had an inverse association with stroke. Global dietary guidelines should be reconsidered in light of these findings.”
Non-systematic reviews:
Annual Review of Nutrition (2015)
Patty W. Siri-Tarino, PhD, Sally Chiu, PhD, Nathalie Bergeron, PhD, and Ronald M. Krauss, PhD, Atherosclerosis Research Program, Children’s Hospital Oakland Research Institute, Oakland, California
Conclusions: “Replacement of SFAs with polyunsaturated fatty acids has been associated with reduced CVD risk, although there is heterogeneity in both fatty acid categories. In contrast, replacement of SFAs with carbohydrates, particularly sugar, has been associated with no improvement or even a worsening of CVD risk…
Replacement of SFAs with CHOs [carbohydrates] has not been associated with benefit and may be associated with increased CVD risk….The effects of various SFA replacement scenarios on CVD risk factors other than lipids and lipoproteins are ambiguous…
The BMJ (Clinical Research ed.) (2015)
R.J. de Souza, Department of Clinical Epidemiology and Biostatistics, McMaster University, Chanchlani Research Centre, McMaster University, A. Mente, Population Health Research Institute, McMaster University, et al.
Conclusion: “Saturated fats are not associated with all cause mortality, CVD, CHD, ischemic stroke, or type 2 diabetes, but the evidence is heterogeneous with methodological limitations.”
“Association of Dietary, Circulating, and Supplement Fatty Acids with Coronary Risk: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis” (on observational data on all fatty acids and RCTs on supplementation with polyunsaturated fats, o3s or o6s)
Annals of Internal Medicine (2014)
Rajiv Chowdhury, MD, PhD, University of Cambridge, Samantha Warnakula, University of Cambridge, et al.
Details: RCT data reviewed is on 105,085 participants; observational data is on roughly 550,000 participants. The RCT analysis combined trials that increased either omega 3s or omega 6s.
Conclusion: “Current evidence does not clearly support cardiovascular guidelines that encourage high consumption of polyunsaturated fatty acids and low consumption of total saturated fats.”
American Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2010)
Siri-Tarino PW, Children’s Hospital, Oakland Research Institute Oakland, Sun Q, MD, Departments of Nutrition and Epidemiology, Harvard School of Public Health, Hu FB, MD, Departments of Nutrition and Epidemiology, Harvard School of Public Health, et al.
Conclusions: “A meta-analysis of prospective epidemiologic studies showed that there is no significant evidence for concluding that dietary saturated fat is associated with an increased risk of CHD or CVD. More data are needed to elucidate whether CVD risks are likely to be influenced by the specific nutrients used to replace saturated fat.”
Meta-analyses and systematic reviews (in chronological order):
“A Systematic Review of the Evidence Supporting a Causal Link Between Dietary Factors and Coronary Heart Disease” (review of observational data and clinical trials)
Archives of Internal Medicine (2009)
Andrew Mente, MA, PhD, Associate Professor, Department of Clinical Epidemiology & Biostatistics, McMaster University, Lawrence de Koning, Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, Pediatrics, University of Calgary, et al.
Conclusions: “The evidence supports a valid association of a limited number of dietary factors and dietary patterns with CHD…. Insufficient evidence (< or =2 criteria) of association is present for intake of supplementary vitamin E and ascorbic acid (vitamin C); saturated and polyunsaturated fatty acids;…”
Non-systematic reviews:
“Saturated Fat, Carbohydrate, and Cardiovascular Disease” (Review of clinical trials)
American Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2010)
Siri-Tarino PW, Children’s Hospital, Oakland Research Institute Oakland, Sun Q, MD, Departments of Nutrition and Epidemiology, Harvard School of Public Health, Hu FB, MD, Departments of Nutrition and Epidemiology, Harvard School of Public Health, et al.
Conclusions: “Although substitution of dietary polyunsaturated fat for saturated fat has been shown to lower CVD risk, there are few epidemiologic or clinical trial data to support a benefit of replacing saturated fat with carbohydrate.”
https://www.nutritioncoalition.us/saturated-fats-do-they-cause-heart-disease
Овощи и их приготовление:
Эффект различных методов приготовления на количество оксалата в овощах.
Бульон
Bone Broth Mineral Content
Bone Broth, Gelatine, Oxalate, and Kidney Stones
Электролиты
Magnesium and stress Magdalena D. Cuciureanu and Robert Vink
Источники кальция и фосфора в Китайской диете (в которой портебляется мало молочных продуктов)
Витамины
The menaquinone (vitamin K2) content of animal products and fermented foods.
Без углеводов нам требуется ~ 10 мг витамина Ц (about 1 lb of muscle meat or 1 oz of liver).
Гипербарическая кислородная терапия
https://www.ketonutrition.org/clinics-clinical-trials-1
Яйца
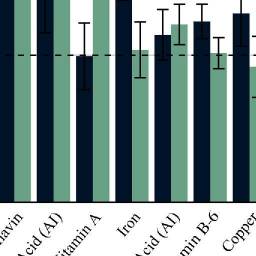

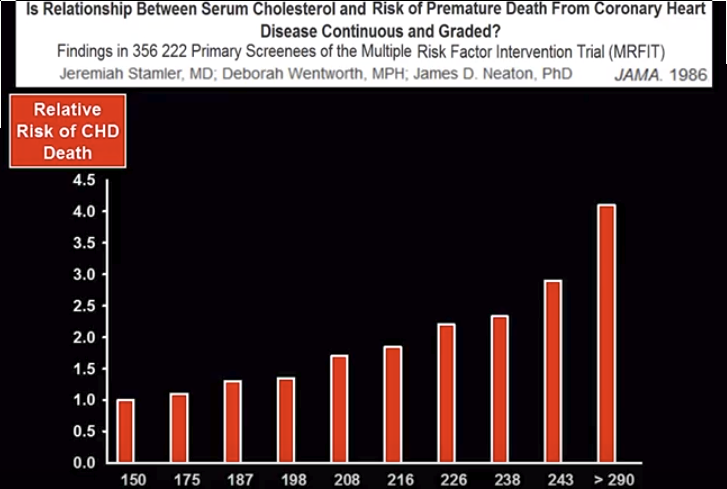
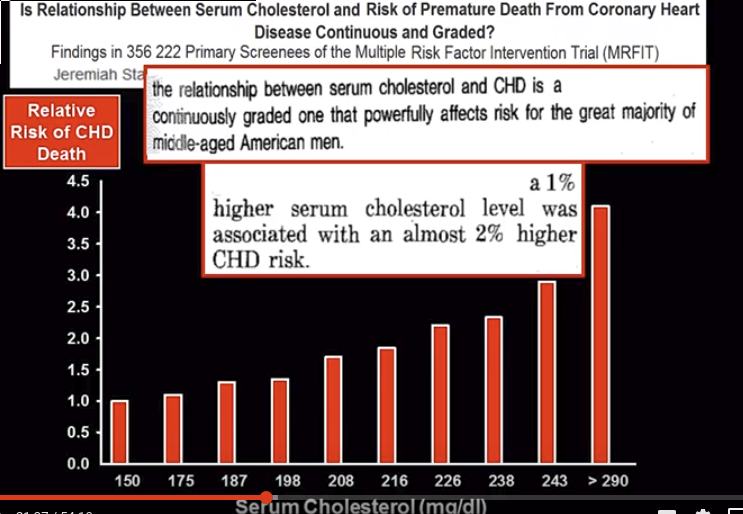
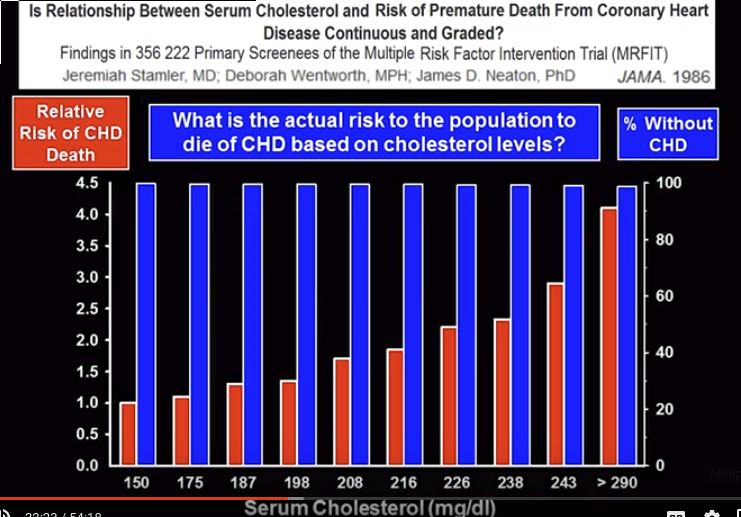
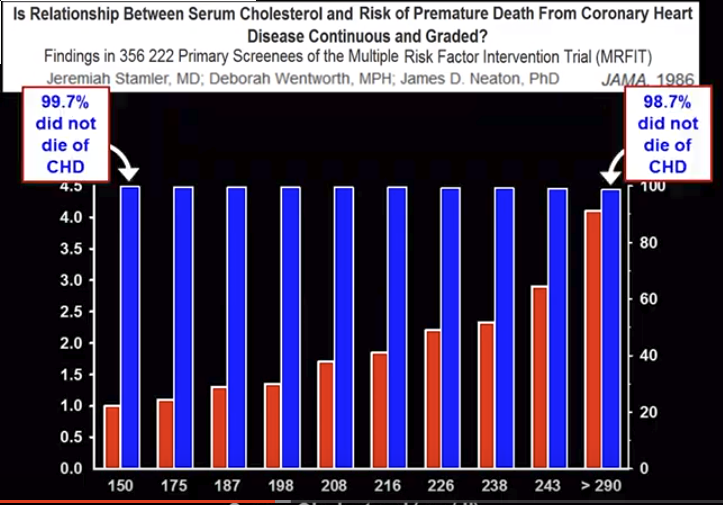
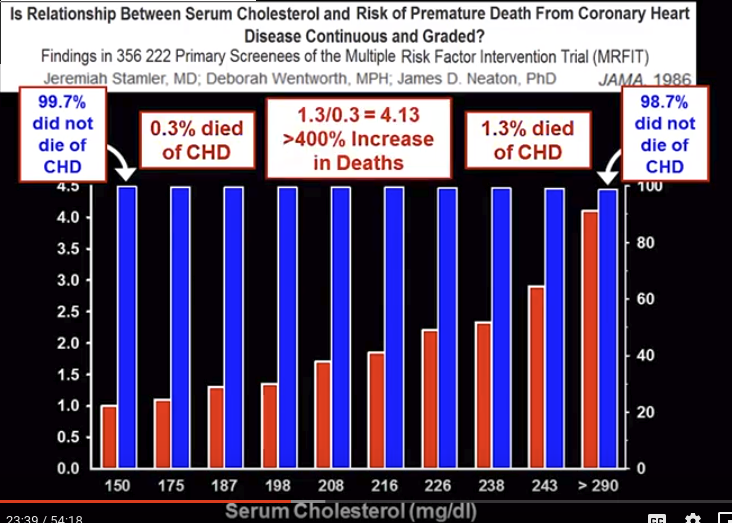
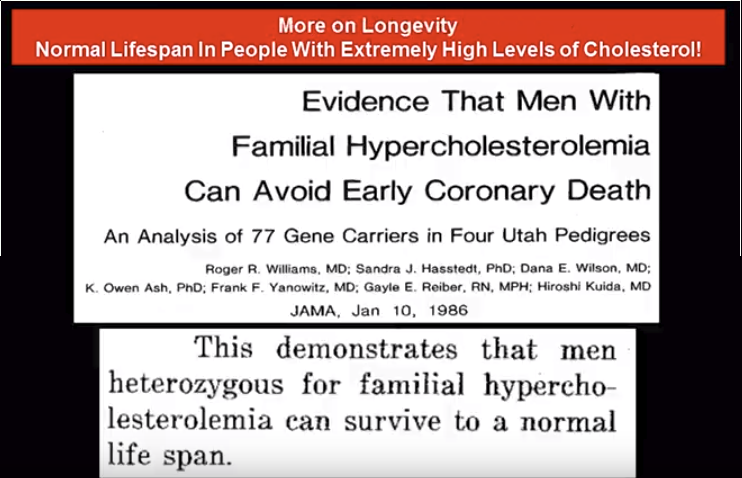
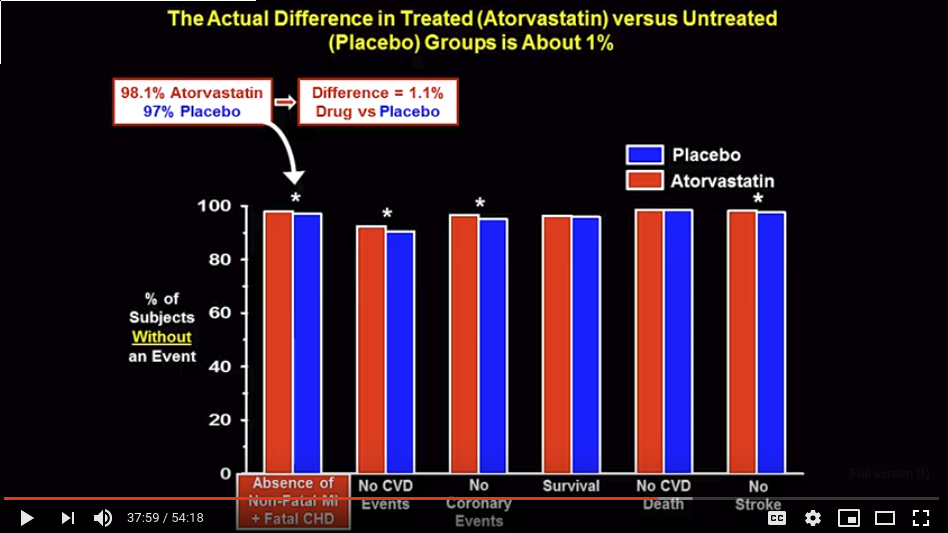
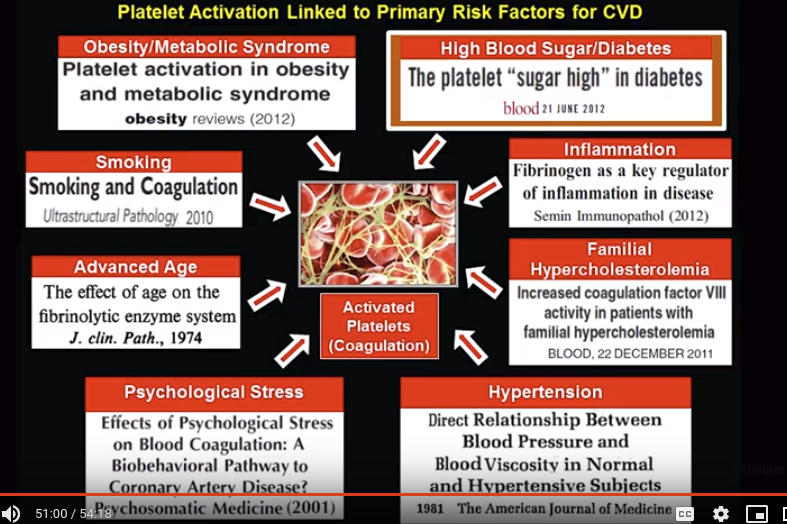
Холестерин
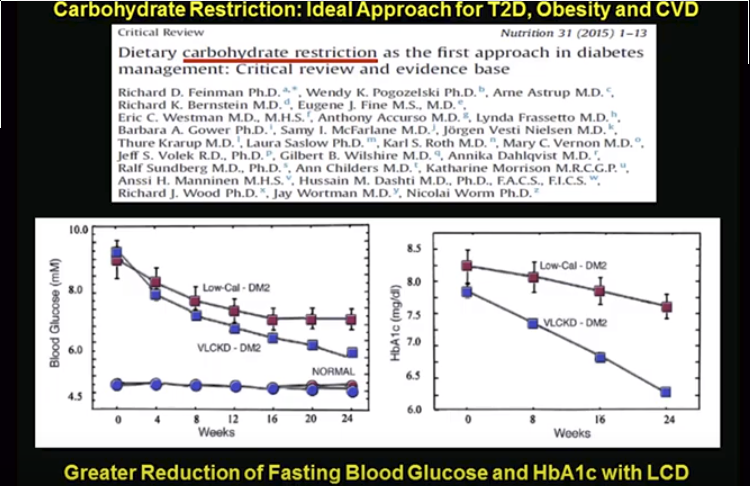
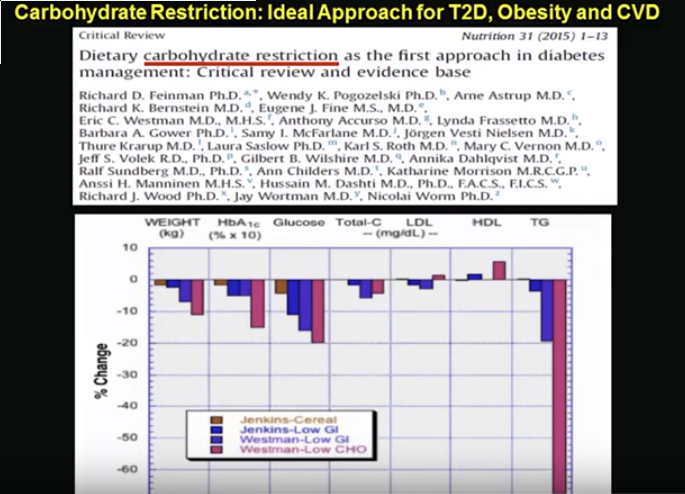

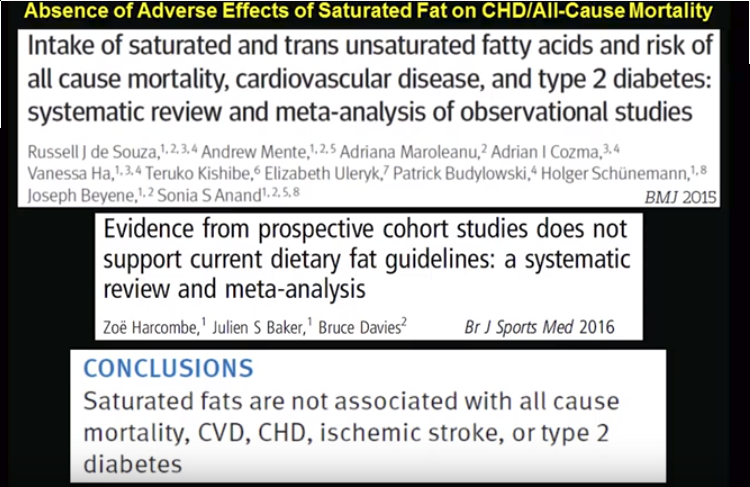










Migraines

Effect of a four-week ketogenic diet on exercise metabolism in CrossFit-trained athletes.